Flood Surveillance System
Introduction
A flood surveillance system is designed to monitor and manage flood-prone areas, providing real-time data, early warnings, and insights to help mitigate flood risks and protect communities and infrastructure. These systems use a combination of sensors, communication technologies, data processing, and visualization tools to detect and respond to potential flooding events. Here are the key components and functions of a flood surveillance system:
Key Features
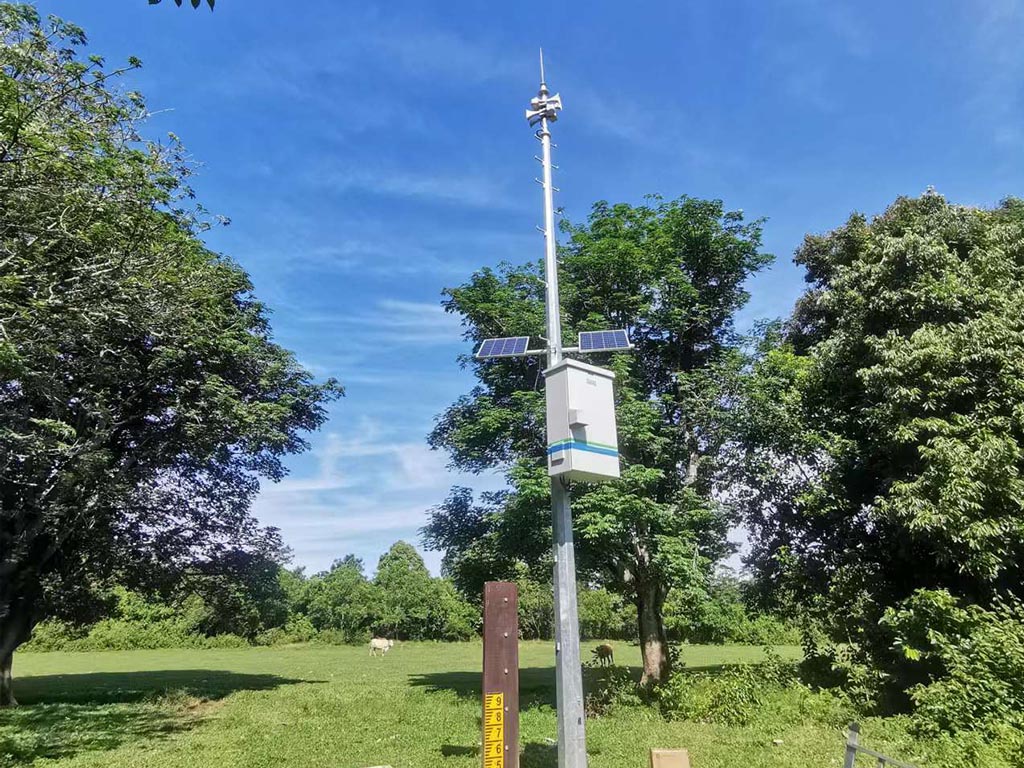
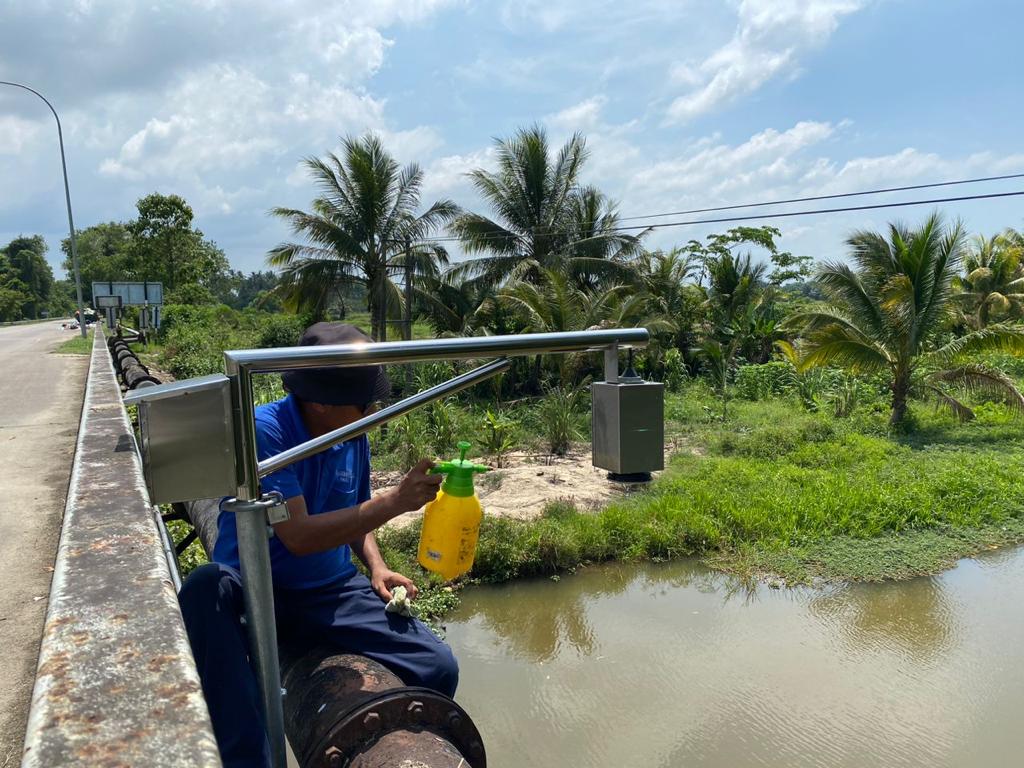
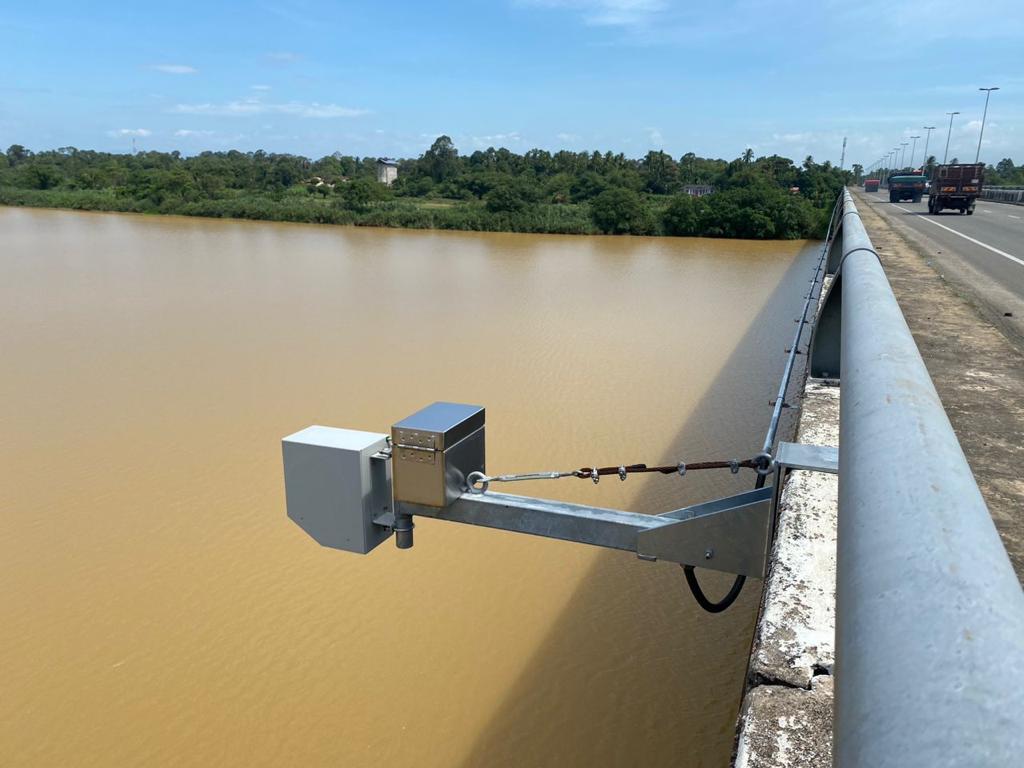
Sensor Network: Flood surveillance systems include a network of sensors that monitor various environmental parameters such as water levels, rainfall intensity, river flow rates, weather conditions, and soil moisture. These sensors are strategically placed in flood-prone areas to collect relevant data.
Data Collection: Sensors collect data in real time and transmit it to a central data repository for processing and analysis.
Data Processing: The collected data is processed and analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and potential flood events. Algorithms and models may be employed to predict flood occurrences based on historical data and current conditions.
Early Warning System: Flood surveillance systems incorporate early warning mechanisms that trigger alerts and notifications when predefined thresholds are exceeded. These alerts are sent to local authorities, emergency services, and residents to ensure timely response and evacuation if necessary.
Public Alerts and Notifications: In addition to alerts sent to authorities, some systems provide public notifications through mobile apps, websites, and social media platforms to keep residents informed and safe.
Historical Data Storage: The system stores historical flood data for analysis, trend identification, and improving prediction accuracy.