Dam Automation & SCADA System
Introduction
Dam automation and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems play a critical role in managing and monitoring dams, reservoirs, and associated infrastructure. These systems combine automation, real-time data collection, control, and visualization to ensure the safe and efficient operation of dam facilities. Here's an overview of their key components and functions:
Key Features
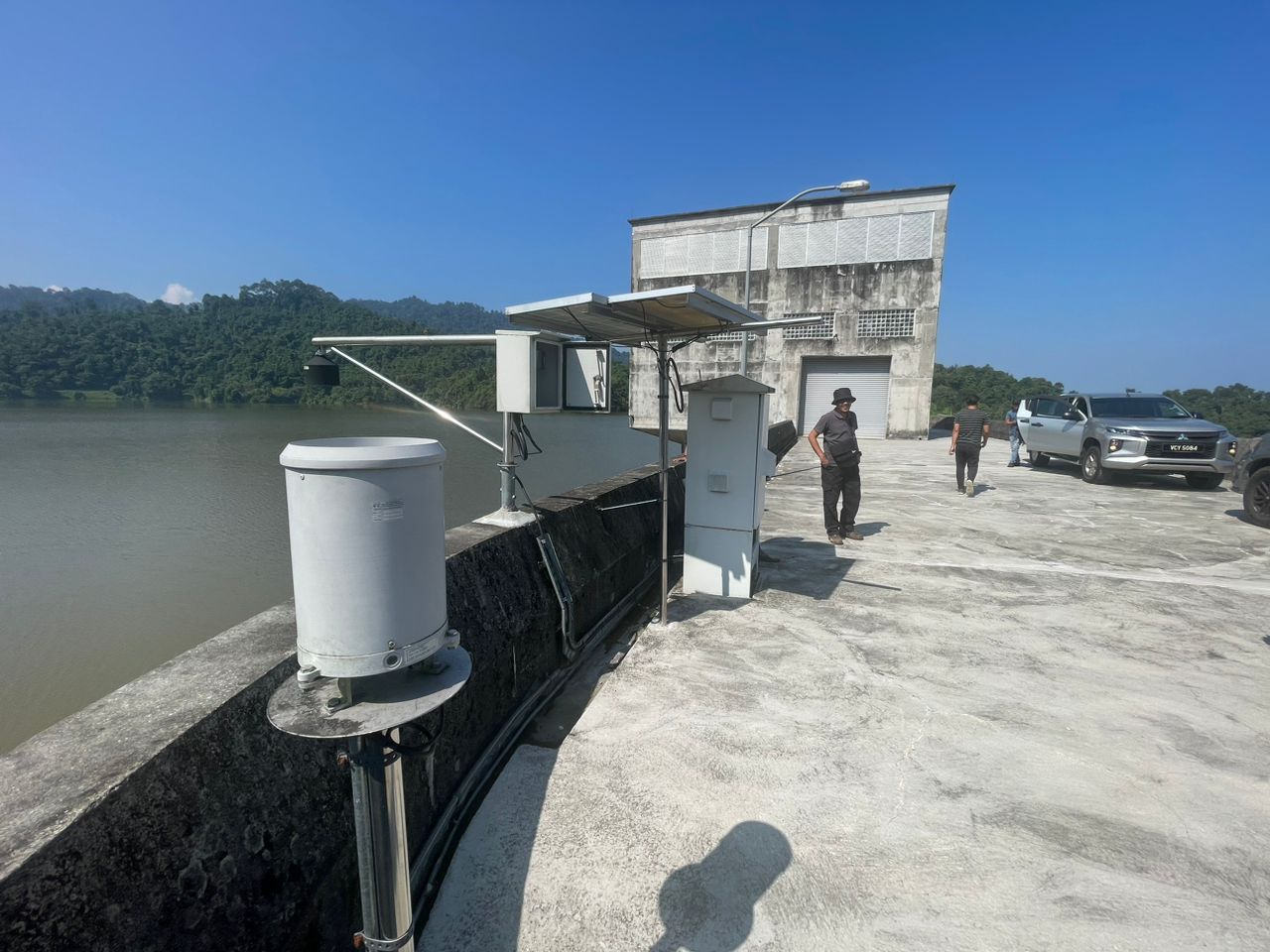
Remote Monitoring and Control: Dam automation and SCADA systems allow operators to remotely monitor and control various aspects of dam operations, such as water levels, gate positions, spillway operations, and more. This reduces the need for constant on-site presence and improves operational efficiency.
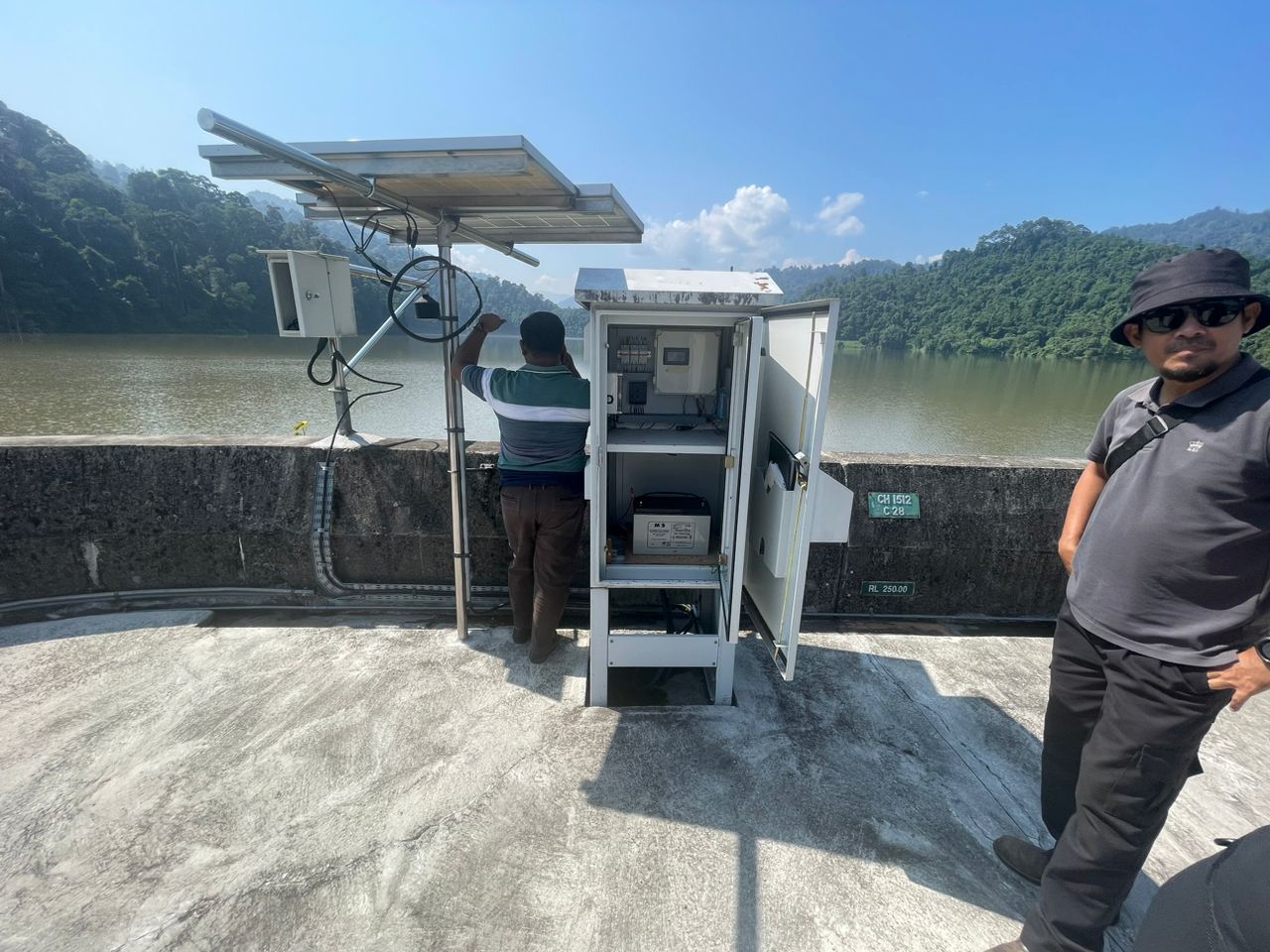
Sensor Integration: These systems integrate a variety of sensors that measure parameters like water levels, flow rates, pressure, temperature, and structural health. The data from these sensors provide real-time insights into dam conditions.
Data Acquisition: SCADA systems collect data from sensors located throughout the dam and its surroundings. This data is then processed, aggregated, and stored for analysis and visualization.
Alarms and Alerts: The system can be configured to trigger alarms and alerts when certain conditions are met, such as high water levels, equipment malfunctions, or potential safety hazards. This ensures that operators are promptly informed of critical situations.
Historical Data Storage: Dam automation systems store historical data, allowing operators to analyze trends, perform root cause analysis, and make informed decisions for maintenance and operation improvements.
Integration with Control Systems: SCADA systems can interface with control systems that allow operators to remotely control dam equipment, such as gates, valves, and turbines, based on real-time data.
Remote Data Access: Authorized personnel can access the SCADA system remotely, which is especially useful for management, regulatory agencies, and experts who need to review data without being on-site.